Use RealVNC or any other VNC tool for remote desktop access¶
qbee.io can securely forward any port from a target edge device to a local machine. It uses qbee-connect or qbee-cli to map the remote port to a local port such that it is securely accessible via localhost:port. This also applies to VNC port 5900 or any other allowing full remote desktop access.
In this way it is very similar to Teamviewer IoT, Anydesk or LogMeIn and a real good alternative. The security layer between the VNC client and server is provided by the secure qbee remote access tunnel. Thus, it can traverse firewalls, NATs and this works even through mobile connections without any static IP address. Since RealVNC is installed in the standard Raspberry PI image this is very easy and fast to test.
In this use case example it is shown how we connect to a remote VNC client on the embedded edge device. For this example we use a Raspberry Pi and RealVNC server as this is already part of the Raspbian image (Raspberry Pi OS). However, any other VNC server will work as well and this works on any platform the agent runs on. On the receiving end we use the RealVNC viewer.
There are a few simple steps to follow:
-
Install a full Raspbian / Raspberry Pi OS image on your Raspberry Pi. This includes a VPN server (RealVNC). Alternatively you can just install the RealVNC server or any other VNC server on your device.
-
Download the agent and bootstrap the device to the qbee platform. Just follow this guide.
-
Enable the VNC server in the Raspberry Pi menu by selecting
enable -
Download and install the RealVNC viewer for your local computer. This runs on Mac OS X, Linux or Windows
-
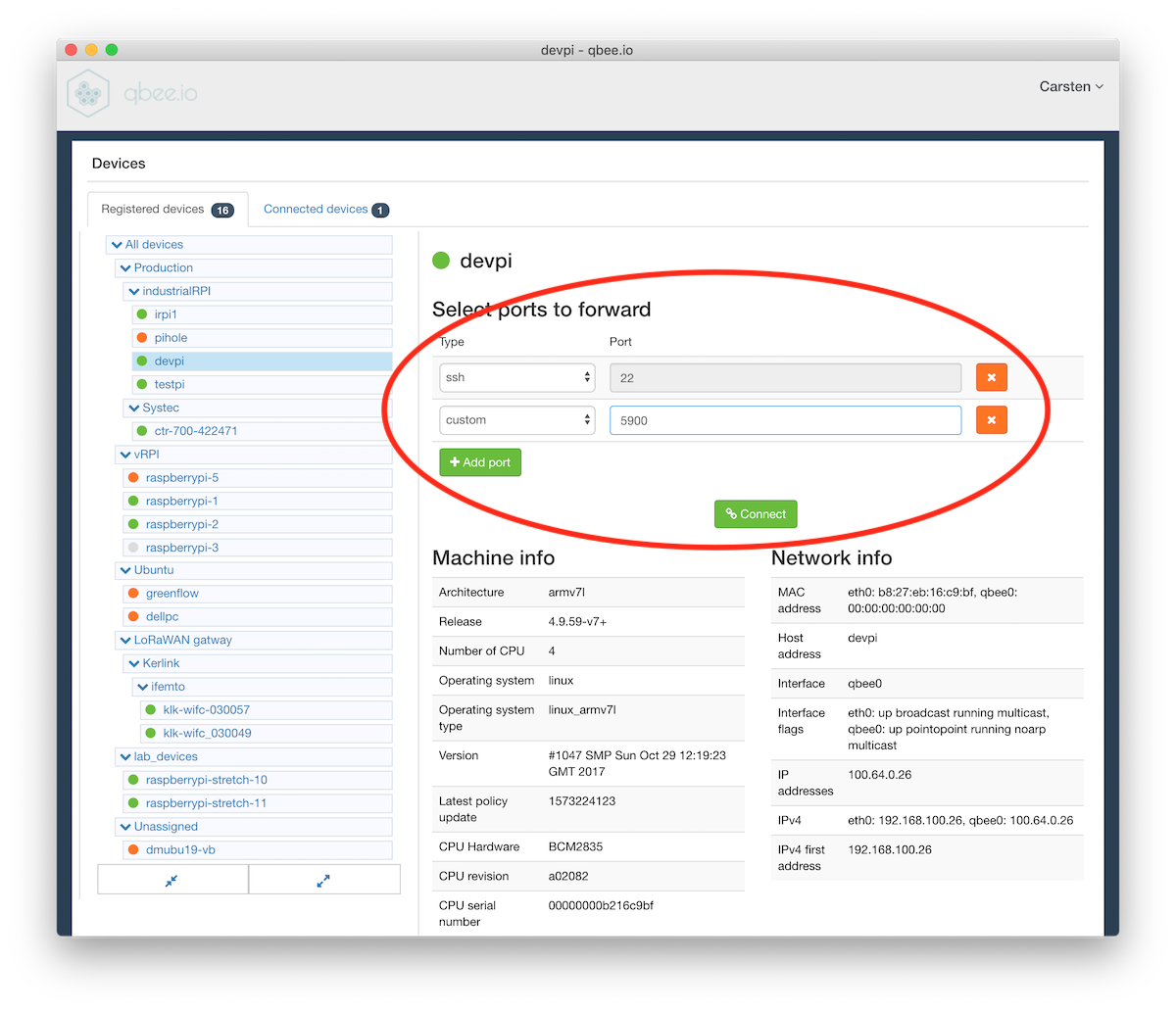
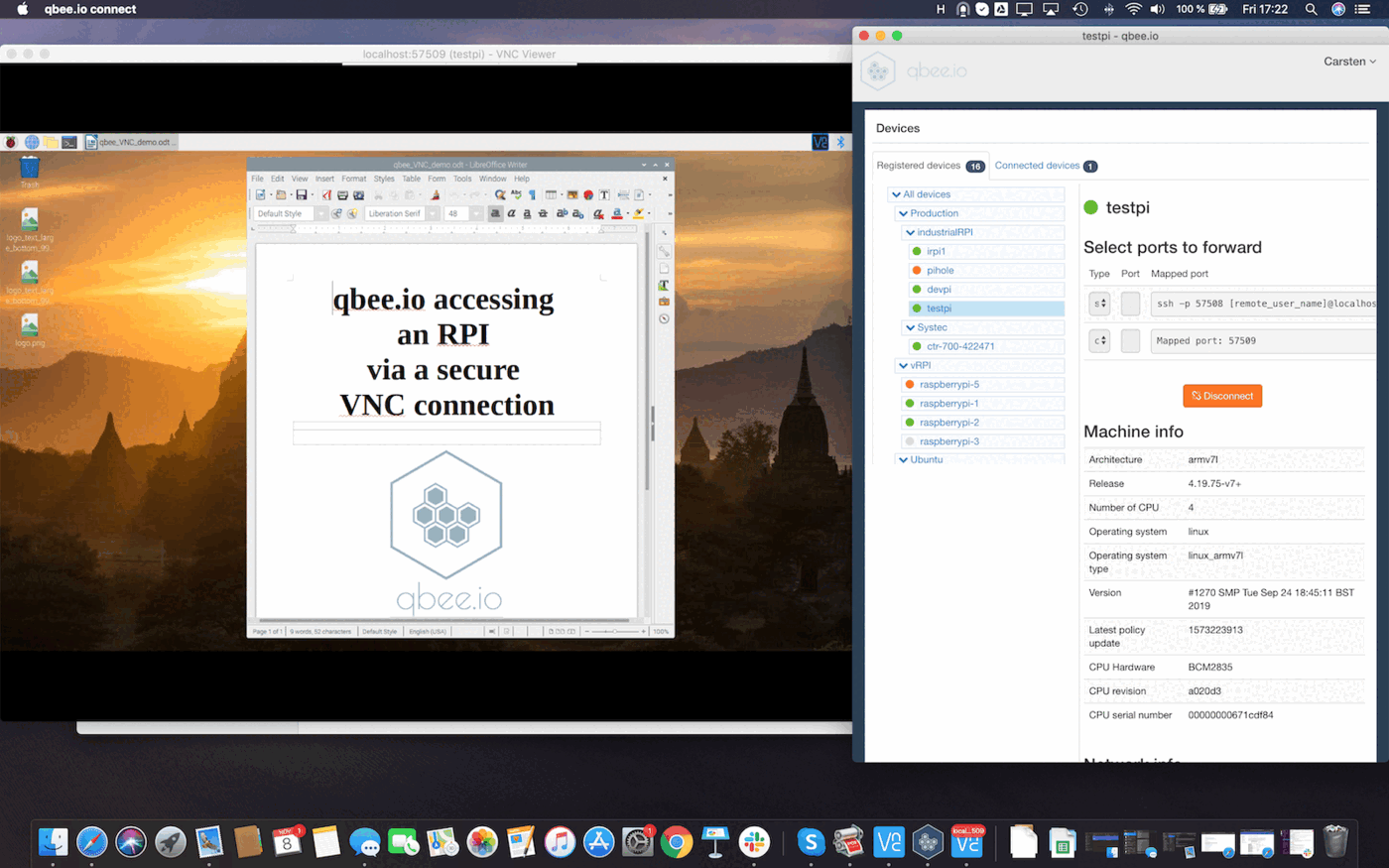
Start qbee-connect (or qbee-cli) on your local computer and select the appropriate device in the tree.
Add a customport 5900for RealVNC (or the according port for your VNC server) and connect.What is the standard VNC port?
RealVNC uses port 5900. Please adjust your port according to VNC server or screen number N (port number + N).
-
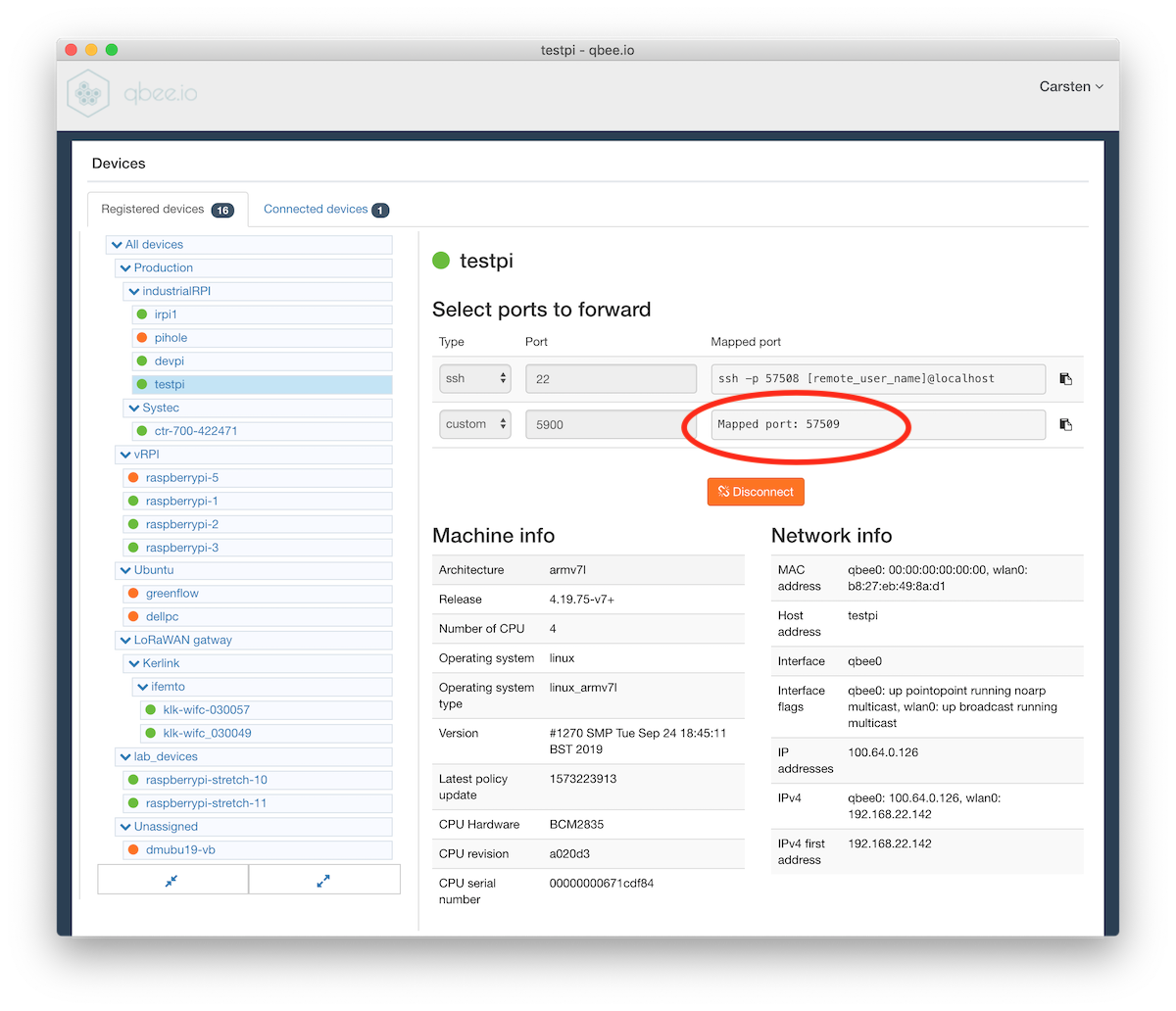
qbee-connect will give you a local mapped port number. In this case this is
port 57509. Press on the copy button to get the port number -
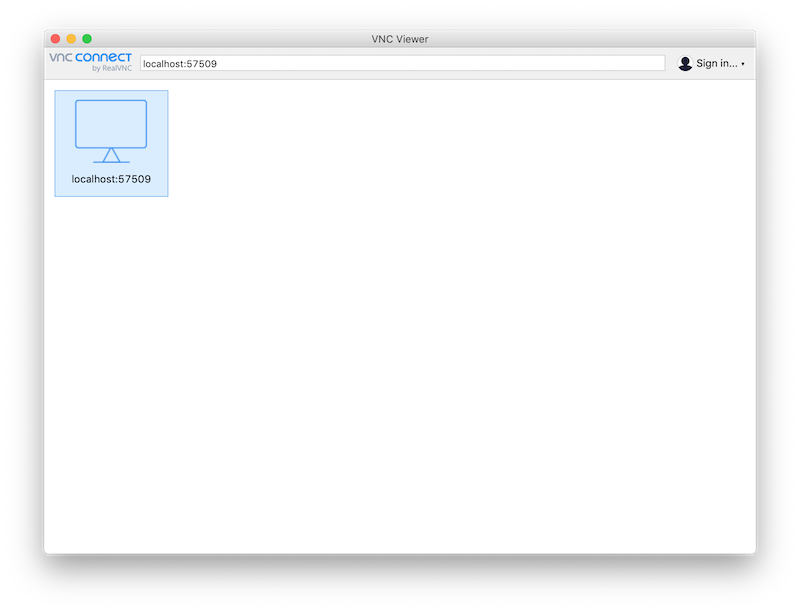
Open RealVNC and connect to
localhost:57509with the port number from the previous step: -
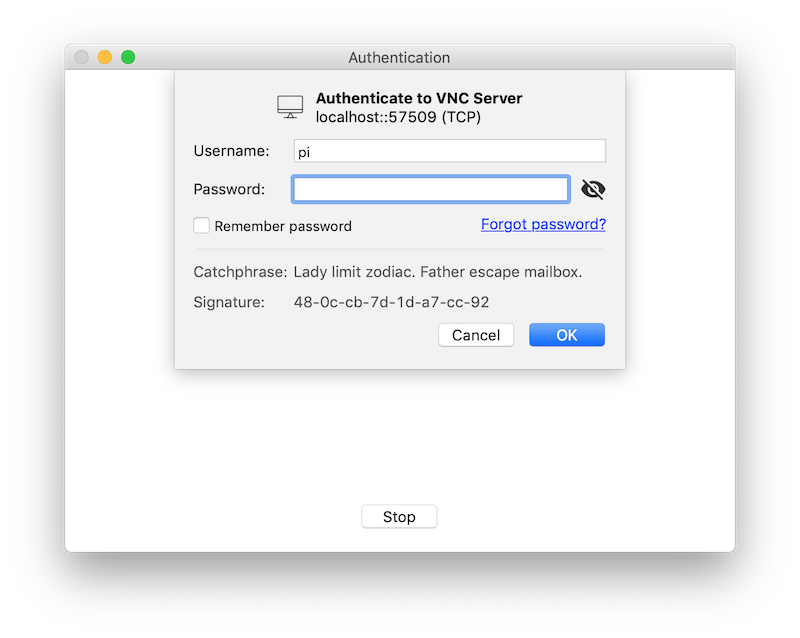
Insert your user name and password and press OK. You can save this as your port will always stay the same.
-
Now you have full secure VNC access to your remote edge device. This solution matches Teamviewer IoT or any of the other alternatives does.
This basically sums up qbee's VNC remote access use case and tutorial. There are a lot of VNC settings to granularly adjust how VNC behaves and make it meet your needs. It is possible to use the RealVNC viewer or any other VNC viewer. Just make sure you find the correct VNC port such as 5900.